1. Design and Operating principle of Piston vacuum pumps :
- The design of Piston vacuum pumps are as shown below
- The design of Piston vacuum pumps are as shown below
- The Operating principle of Piston vacuum pumps : Its principle is that of the classical positive-displacement pump, The operating principle of piston vacuum pumps is one of the oldest in the history of vacuum generation. The father of vacuum technology is Otto von Guericke ,used a pump incorporating this design for his experiments.
Also like diaphragm pumps, an inlet valve as well as an outlet valve for classical piston vacuum pumps. The arrangement of these valves produces a dead volume above the piston in the cylinder head, which limits the maximum compression ratio. Moreover, ultimate pressure is limited by the force that must be applied to open the inlet valve, these two disadvantages are avoided through the special design of the piston pump described below.
Due to new materials pairings, without oil between the piston seals-4 and the cylinder wall when operation. Since the entire cross section of the cylinder is formed as an outlet valve plate-5, the harmful space (dead volume) between the piston-2 and the cylinder head tends toward zero.
A crankshaft-driven connecting rod moves a piston up and down in a cylinder. The inlet flange-1 communicates with the swept volume via the intake holes-3 when the piston-2 is in its bottom-most position, as the piston moves upward, the inlet holes-3 close off again, and the incoming gas is compressed, after reaching the opening pressure, the valve plate-5 lifts and the gas flows to the inlet holes-3 of the second stage via the overflow channel-7 and the crankcase housing, the second seal-4 prevents the inlet channel from communicating with the crankcase during the compression stroke, the second stage operates in the same manner as the first, and discharges the gas to the atmosphere via the outlet channel-10 and the silencer-11.
Gas ballast air can be admitted to the crankcase via the gas ballast valve and the throttling port behind it in order to displace water vapor though the pump without condensation
If dry piston pumps, wear occurs on the piston seals during operation, particularly at high average piston speeds, once the required inlet pressure is reached, seal wear can be significantly reduced by lowering the RPM.
2. Applications of Piston vacuum pumps:
If for compare Diaphragm vacuum pump, dry piston pumps have higher pumping speeds, as well as are used where a clean, hydrocarbon-free vacuum is required when operating near ultimate pressure.
Also like all true positive-displacement pumps, piston vacuum pumps have the same pumping speed for all gases.
Piston vacuum pumps are suitable for use as dry backing pumps for turbomolecular pumps. But to prevent enrichment of hydrogen as well as water vapor in the backing vacuum area of the turbo-pump, should use gas ballast if necessary.
Piston pumps are especially suited to analytical applications as well as for leak detectors, if the test specimens are directly evacuated by the backing pump for leak detection, they cannot be contaminated with oil vapor when a dry backing pump is used, piston pumps are not suitable for pumping corrosive , abrasive media
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Twitter
Twitter
 12:03 AM
12:03 AM
 Thì Trần
Thì Trần

 Posted in
Posted in 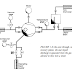









Piston vacuum pumps
ReplyDelete